Canada’s Unemployment Rate Hits 7%: What It Means for You and the Markets
Canada’s May 2025 Unemployment Rate Hits 7%: What It Means for You and the Markets
By: Rushit Goyani, RFRA
In May 2025, Canada’s unemployment rate rose to 7.0%, the highest in nine years outside the pandemic. This signals a slowing job market, with more people looking for work and fewer new jobs being created.
What Is the Unemployment Rate?
The unemployment rate shows the percentage of people in the labor force who are jobless but actively looking for work. It is a key economic signal used to measure how strong or weak the job market is at any time.
What Happened in May 2025?
Unemployment rose slightly from 6.9% in April to 7.0% in May, meaning job growth is no longer keeping up with population growth. While some jobs were added overall, key industries like manufacturing lost positions due to economic pressures, including U.S. trade tariffs.
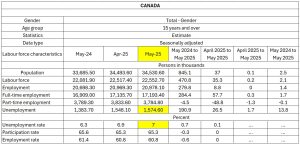
Source: – Statistic Canda
More Canadians are staying unemployed for longer, with the average job search now taking over 21 weeks. That is a clear sign the labor market is tightening, and opportunities are becoming harder to find. Below is a month-on-month comparison for unemployment data.
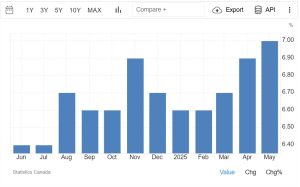
Source: Trading Economics / Statistics Canada
In Canada, an increase in the unemployment rate is generally seen as a sign of economic weakening, often prompting the Bank of Canada to reassess its monetary policy stance. This trend indicates that job creation is not keeping pace with the country’s growing population, suggesting a cooling labour market.
To counteract such economic slowdowns, the Bank of Canada may opt to lower its benchmark interest rate in an effort to encourage borrowing, spur investment, and drive employment growth. However, this strategy must be weighed against the potential for inflation. For example, as of June 2025, the Bank chose to hold its key rate steady at 2.75%, despite signs of an economic slowdown. This decision was largely influenced by the uptick in core inflation, which had climbed to 3.15% in April, exceeding the central bank’s comfort zone.
This cautious approach highlights the challenges involved in setting monetary policy amid mixed economic signals. Although rising unemployment would usually justify easing interest rates, sustained inflation can limit the Bank’s flexibility. Consequently, the Bank of Canada must navigate a delicate balance, factoring in a range of economic indicators to ensure financial stability and support long-term growth.
Below is a long-term chart of the unemployment rate, interest rate, and GDP growth rate.
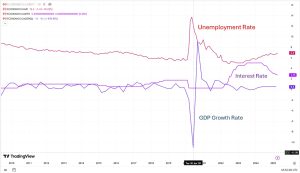
Why It Matters: Bonds and Stocks
Bond Market Effects
When unemployment rises, central banks may lower interest rates to support the economy. Lower rates tend to boost bond prices, as investors shift to safer, more stable returns during uncertain times.
Stock Market Effects
Higher unemployment can hurt company profits, as fewer people working means lower consumer spending. But if markets expect interest rate cuts, that could help stocks rise by making borrowing cheaper and boosting confidence.
Key Takeaways
- 7.0% unemployment shows Canada’s economy is slowing and job creation is not keeping pace.
This may lead the Bank of Canada to adjust interest rates to avoid further economic weakening. - Bond markets often respond positively to rising unemployment because it suggests future rate cuts.
As a result, bond investors may see rising prices if the central bank shifts to a more supportive stance. - Stock markets face uncertainty, balancing the negative effect of weaker earnings with the potential benefit of lower interest rates.
The reaction depends on whether investors believe the slowdown is short-term or a longer economic trend. - Investors should watch for Bank of Canada updates and labor market trends.
These signals help forecast economic direction and how both bonds and stocks might behave.
Bottom line: Canada’s rising unemployment rate is a sign of economic slowdown. It affects everyday people, financial markets, and policy decisions—so it is a number worth watching.






 By: Shawn Todd CFP
By: Shawn Todd CFP